Resources
Case Studies
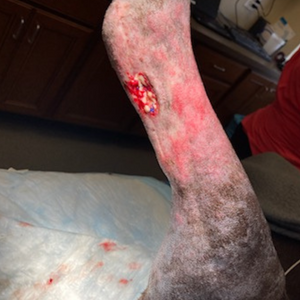
Torn Left Hind Achilles
Amanda Conkling, DVM, DACVS | BluePearl Pet Hospital Grand Rapids
Case Details
History:
Dog diagnosed with probable torn Achilles in March and treated with Gabapentin and Galliprant. Dog had previously torn CCL on RH and has a history of seizures. Toe touching lameness progressed into flattening of the left hind limb and dog was referred for potential surgical correction.
Diagnosis:
- Achilles tendon rupture – left complete, degenerative, possibly early right degeneration
- Cranial cruciate ligament tear – right extracapsular stabilization with persistent instability
Surgical Treatment Timeline:
The tendon was debrided and repaired by reattaching to the calcaneous. The repair site was wrapped in porcine collagen sheeting and injected with PRP to aid in healing. A screw was placed from calcaneous into tibia/fibula to maintain the tarsus in extension. Cast placed, recheck in one week.
9 Days Post-op: Grade III/IV lame in left and right rear limbs. Left cast in place, purulent discharge noted from incision. Culture obtained and cast replaced with a mepilex bandage. Right stifle remains unstable.
Culture confirmed surgical site infection, patient prescribed Baytril and Chloramphenicol. Bandage was intact and incision was intact with serosanguinous drainage. Calcaneal tendon and tibiocalcaneal screw palpated stable.
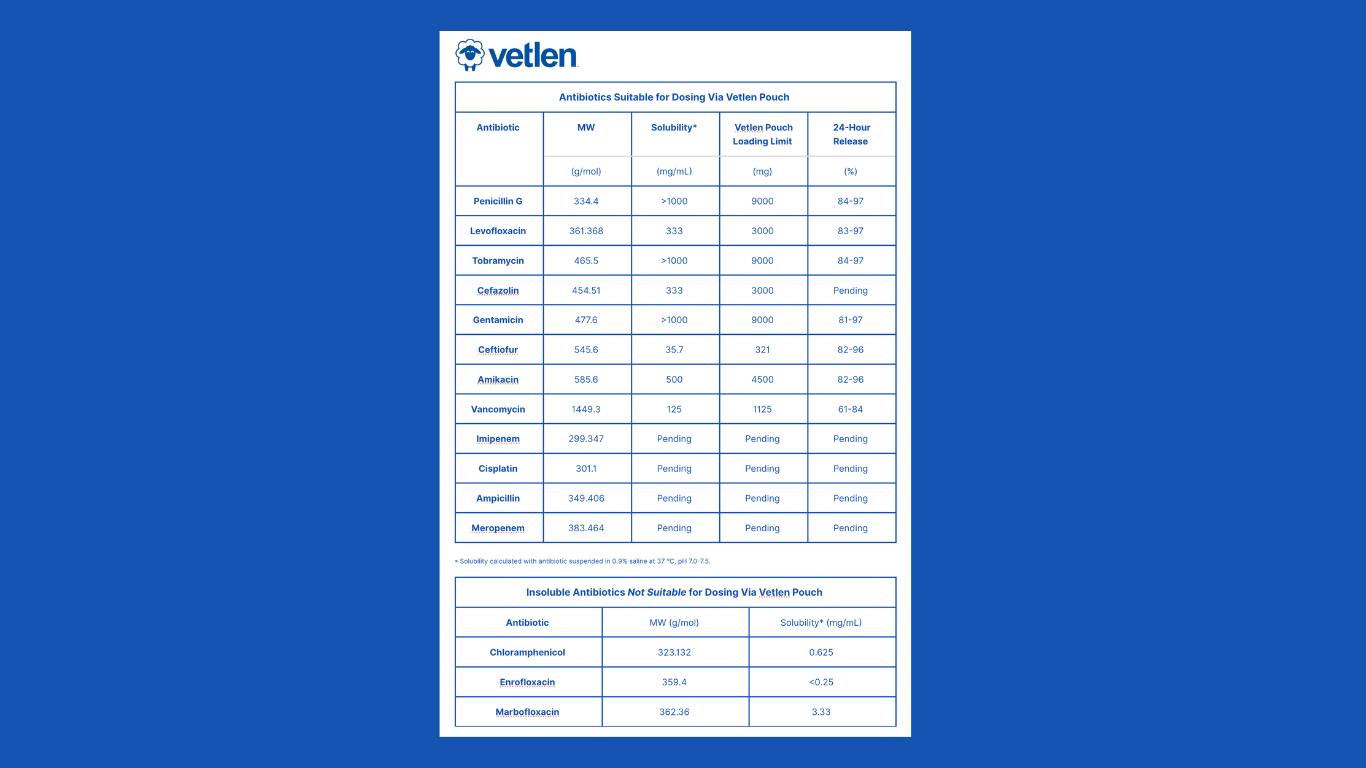
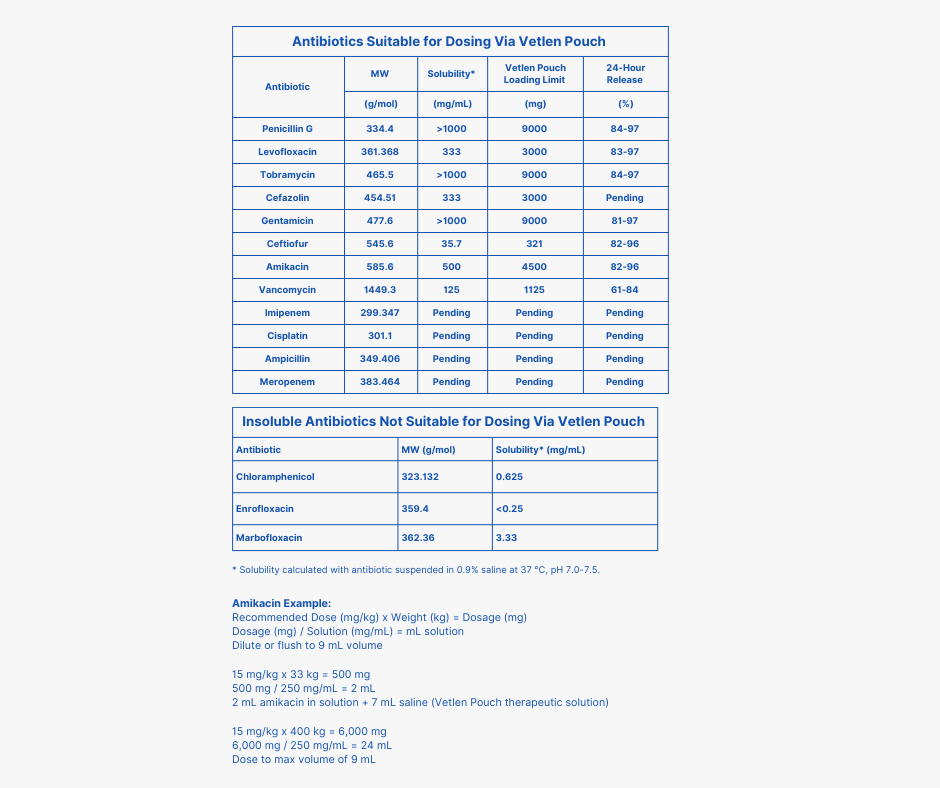
21 Days Post-op: Surgical site infection persisted and patients experienced intermittent vomiting and reduced appetite. Chloramphenicol discontinued and replaced with amikacin 750mg SC SID for 10 days.
36 Days Post-Achilles Repair: Dog underwent TPLO surgery for right hind CCL repair.
42 Days Post-Achilles Repair: A draining tract was present on the lateral aspect of the tarsus and the tissue around it was swollen. Culture taken and radiographs revealed lysis of the calcaneus due to suspected osteomyelitis. The tibiocalcaneal screw was intact. Amikacin 750mg SC SID prescribed.
47 Days Post-Achilles Repair:
Implant removed and Kerrier beads placed
Calcaneal screw was removed, screw was loose. Tendon palpated intact with sutures and discolored periseal visualized. Numerable amikacin Kerrier beads placed in the screw tract and around the site to capacity. Cast replaced.
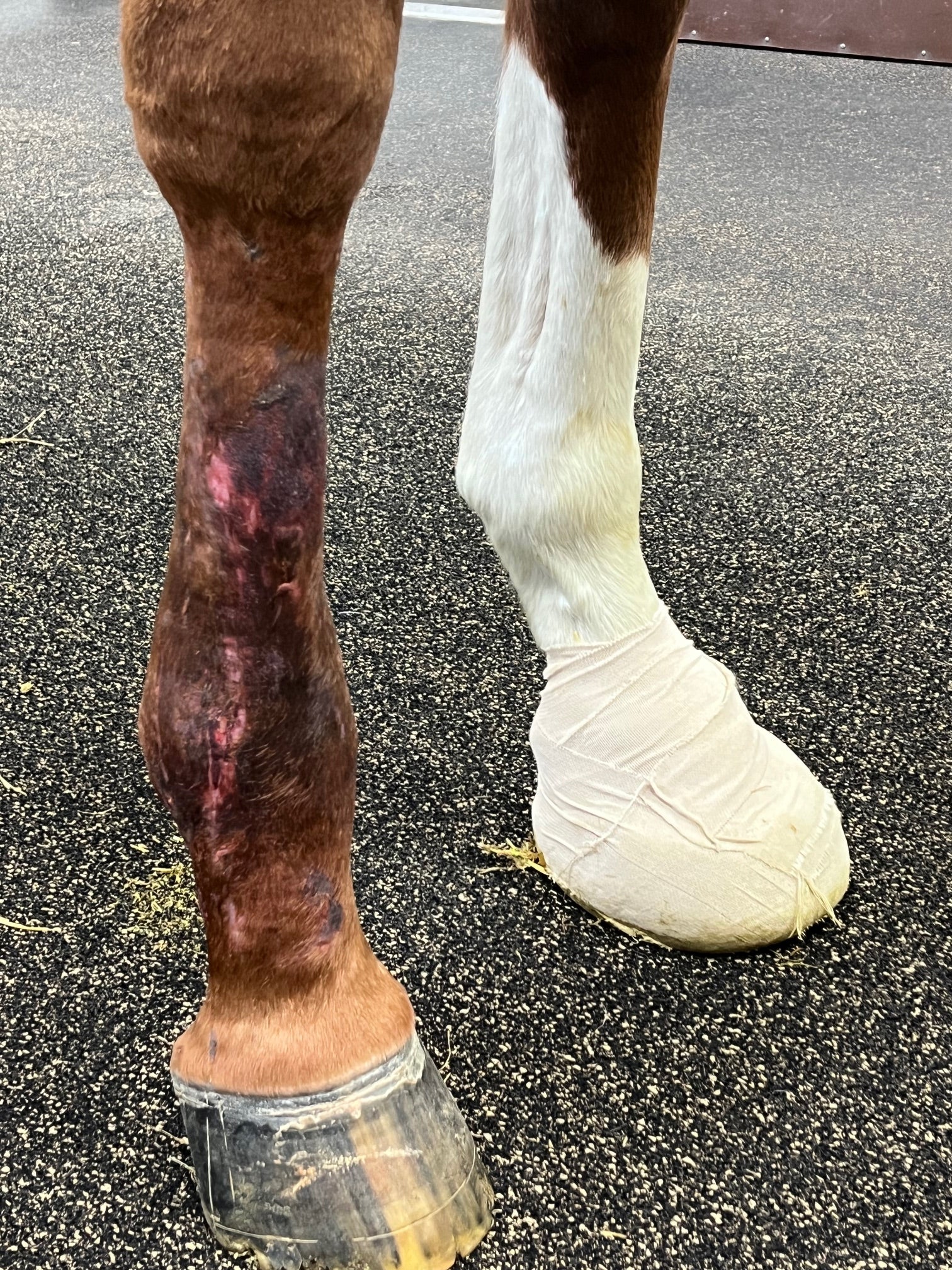
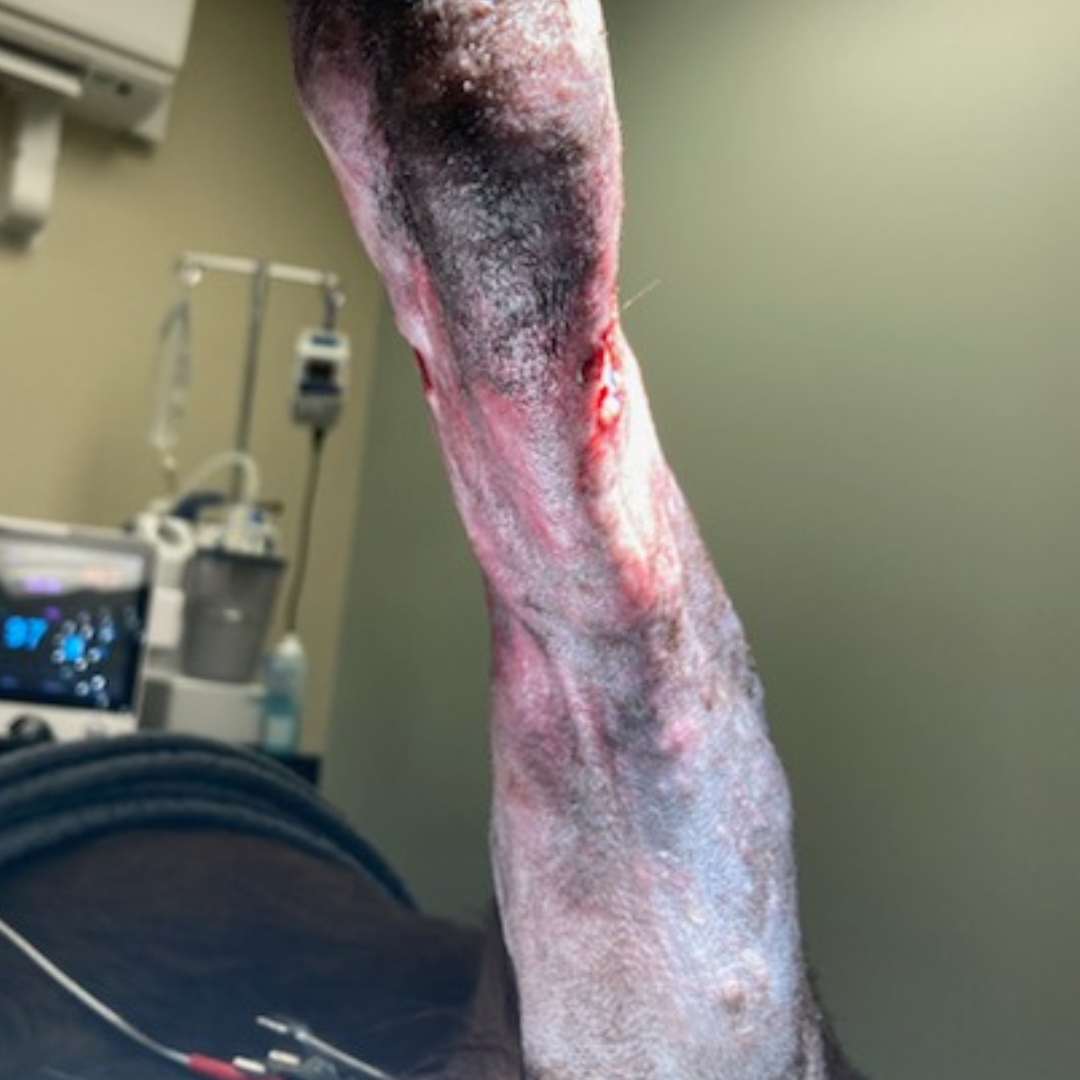
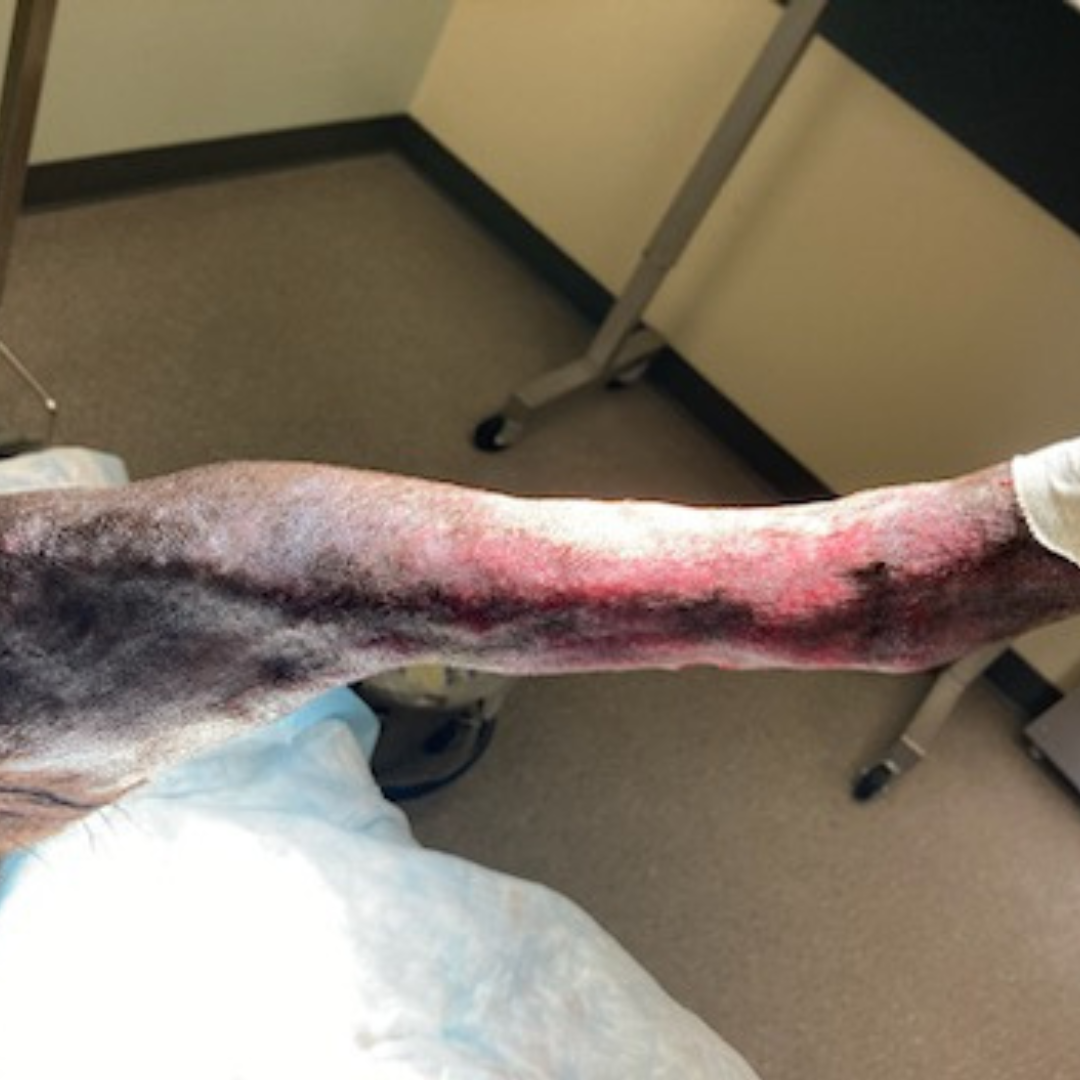
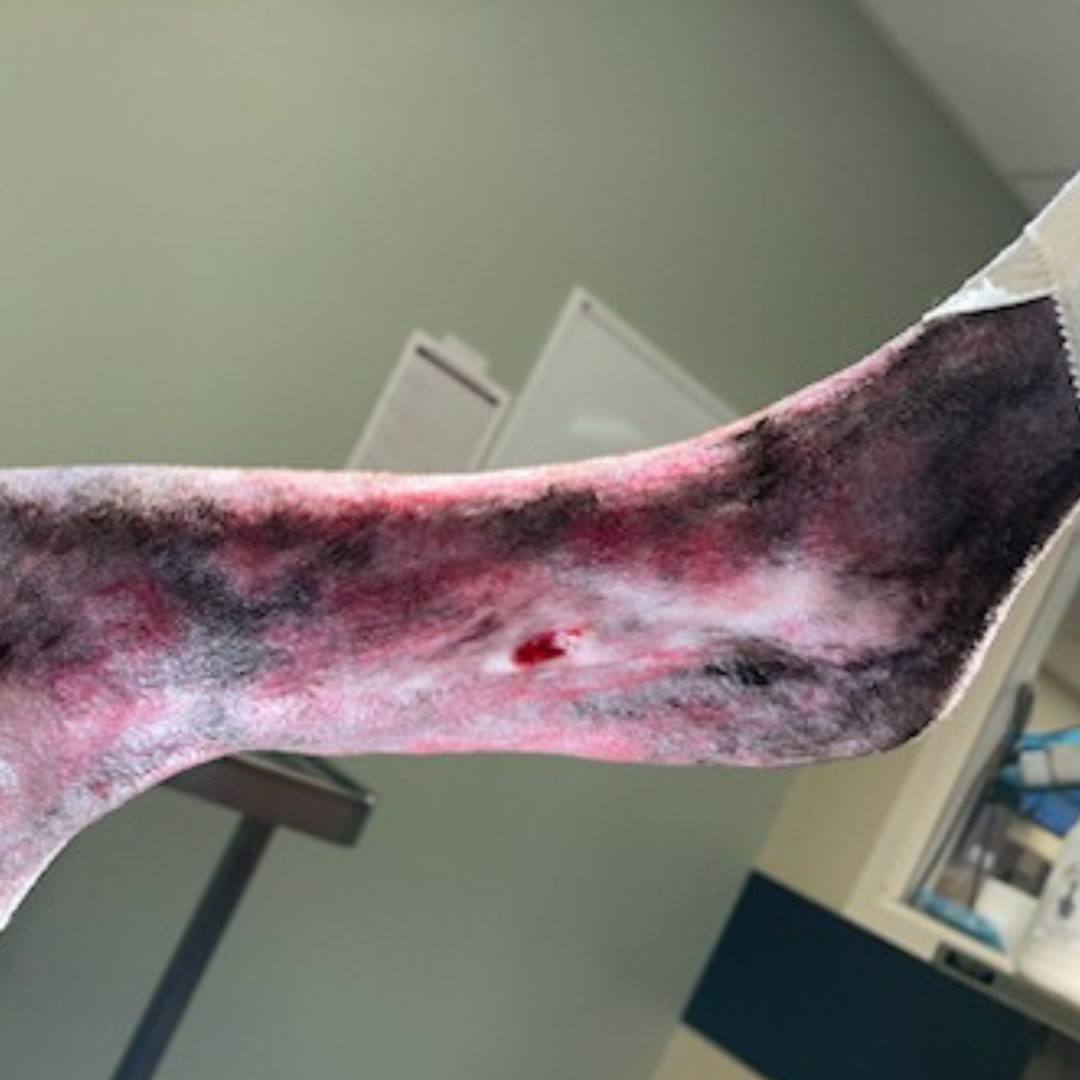
15 Days Post-Bead Placement, 62 Days Post-Achilles Repair: Cast removed with marked malodorous discharge from proximal incision, purulent with beads being extruded. Culture obtained, site cleaned, and honey bandage placed with lateral component of splint. Owner advised if infection cannot be controlled, aggressive debridement and long-term support via custom orthotic or pantarsal arthrodesis once infection is 100% cleared.
43 Days Post-Bead Placement, 90 Days Post-Achilles Repair: Multiple rechecks over the last 30 days show persistent infection with the Kerrier beads extruding. Grade III/IV lame left rear limb with plantigrade stance and persistent purulent discharge from proximal aspect of the lateral hock incision and strike through on the bandage. Recommend custom orthotic brace and re-cultured to determine treatment plan.
48 Days Post-bead Placement, 95 Days Post-Achilles Repair
Vetlen Pouch Placement to Treat MSRP Infection and Implant Removal
Under brief anesthesia, a lateral approach to the left Achilles was performed. The previously placed periseal and all identifiable prolene sutures were removed. Copious lavage and sponge debridement. A Vetlen Pouch was placed and the tube exited proximal lateral tibia. Pouch secured via 3-0 PDS distal tacking suture and tube secured via tacking sutures. Site closed via 3-0 PDS SC and skin staples. Vetlen Pouch doses with 750 mg of amikacin daily.
15 Days Post- Vetlen Pouch Placement: The pouch was removed without incident, with some of the pouch already migrating out of the wound.
11 Weeks Post Implant Removal: Grade I/IV lame, patient stable with custom orthotic. No sign of infection.
Assessment: The Vetlen Pouch was very easy to place (similar to any JP drain) and simple for owners to use at home with the daily injections. It was very well tolerated by the dog in this case.
Images
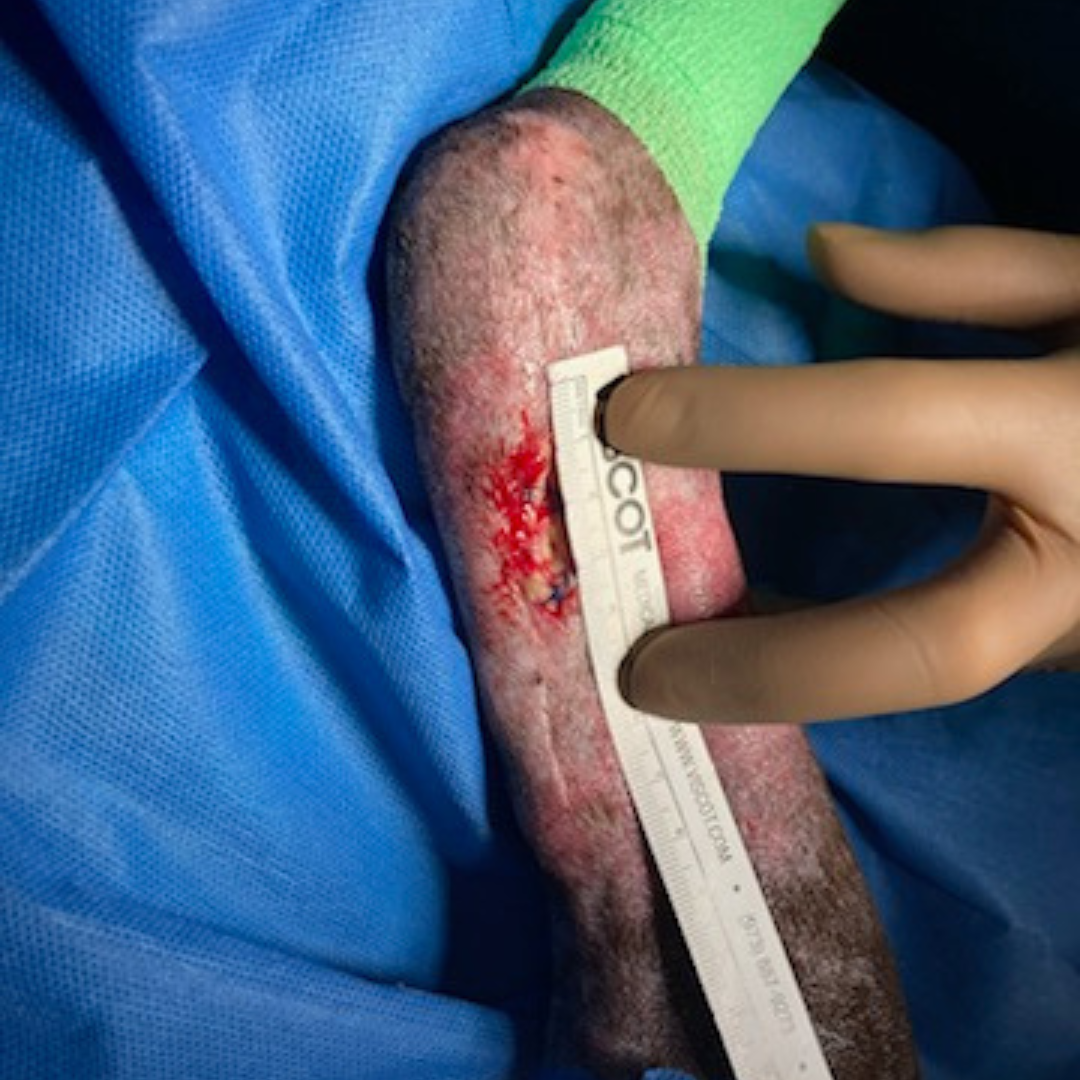
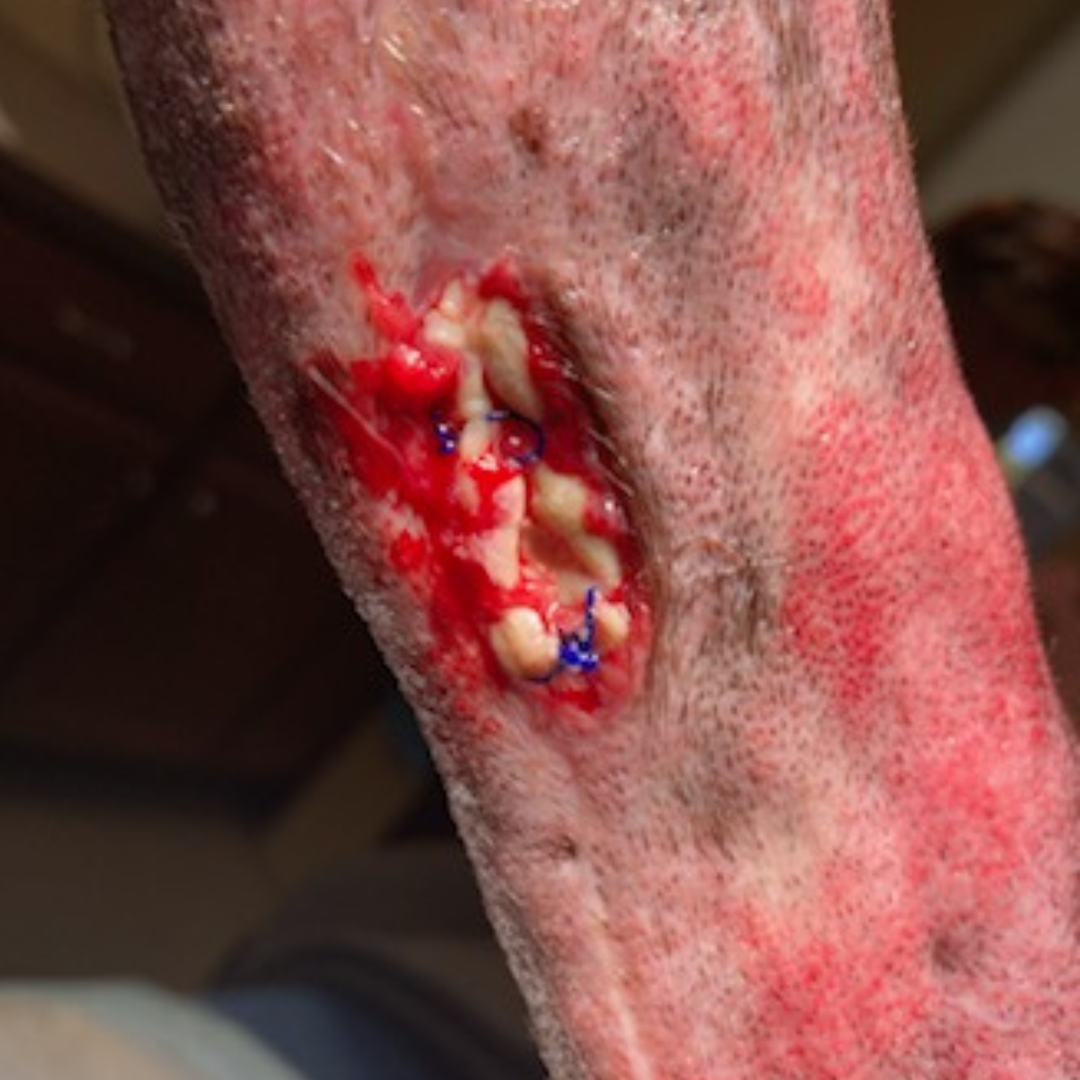
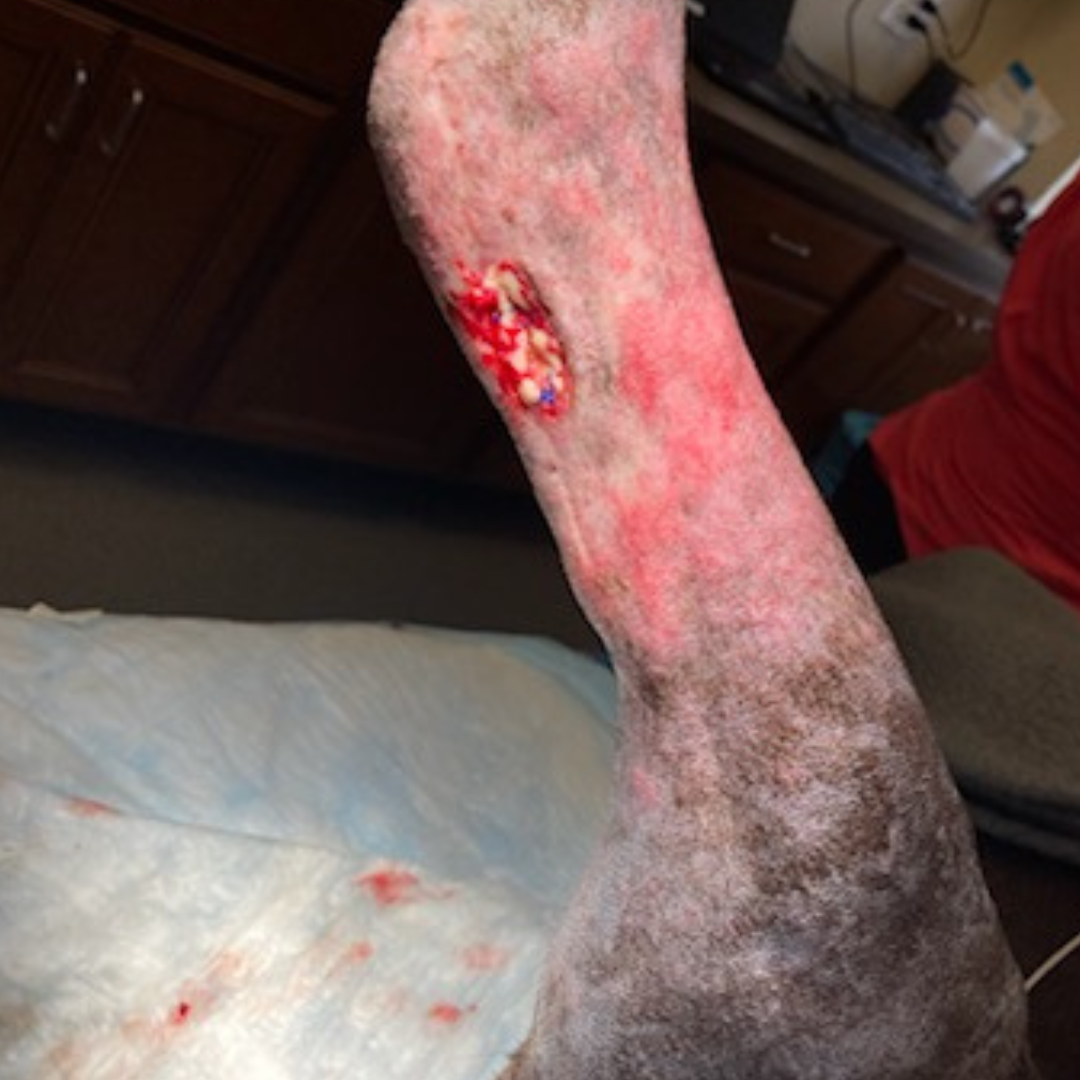
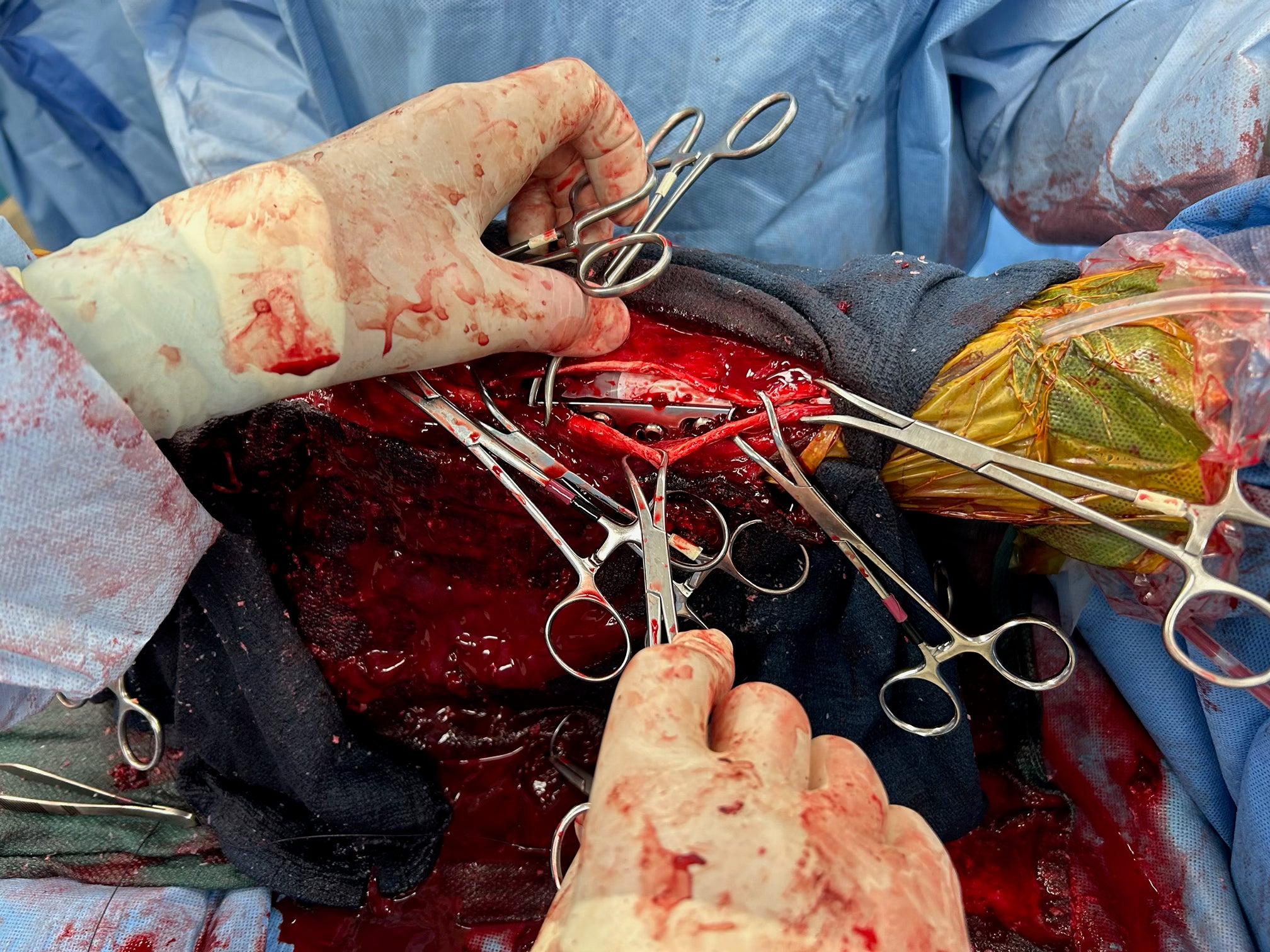
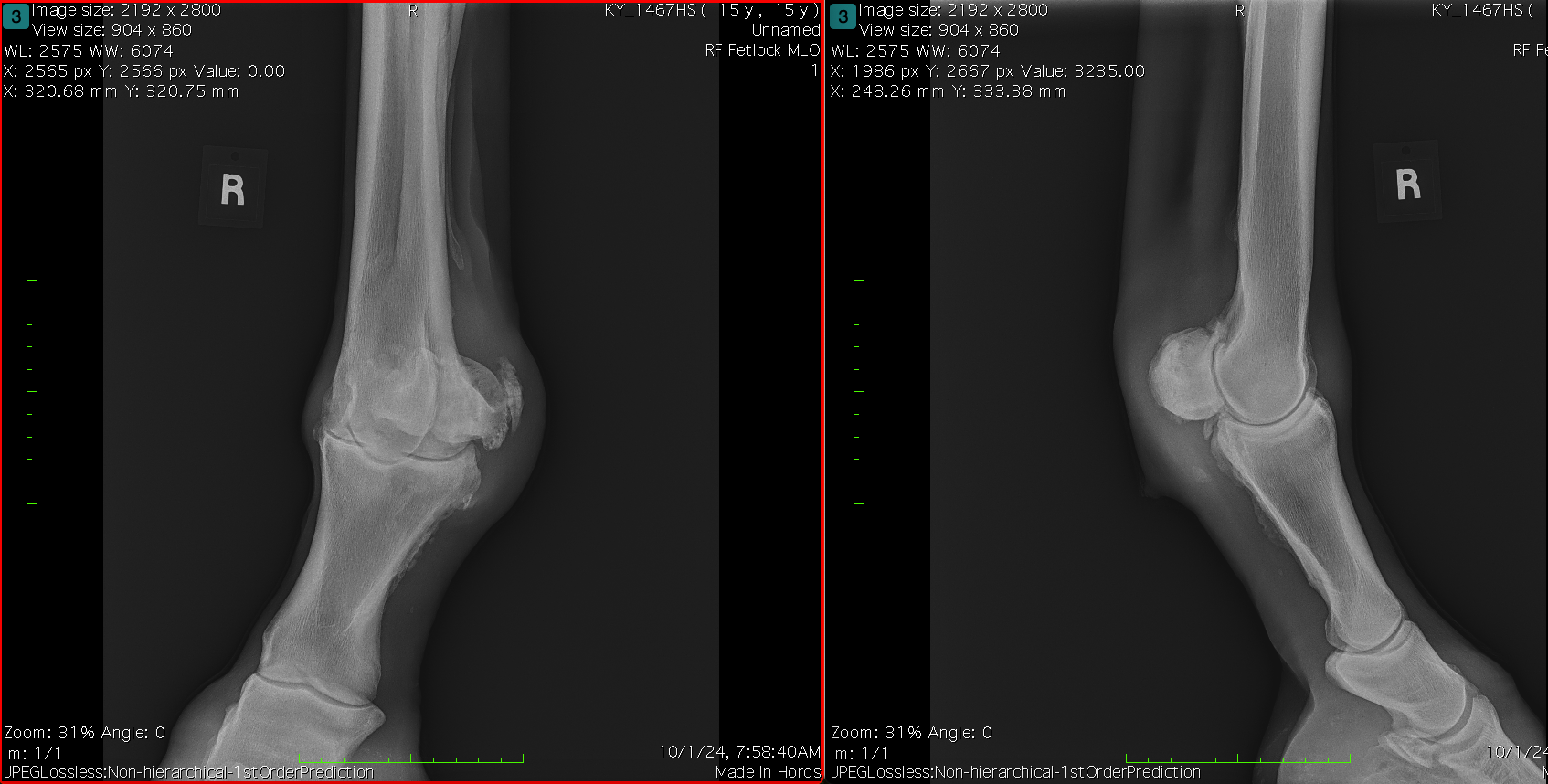
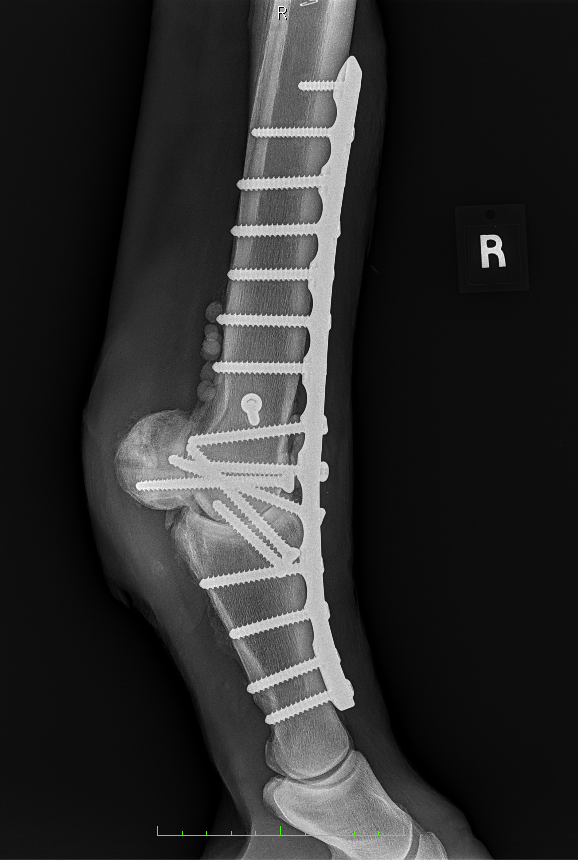
Fetlock Arthrodesis Due To Degenerative Arthritis
| Rood and Riddle
Case Details
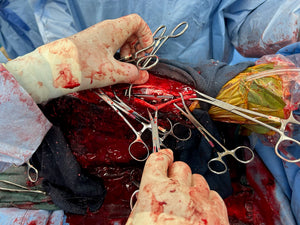
Diagnosis and Procedure: Degenerative arthritis of the fetlock joint, pain leading to overloading the other foot. Fetlock arthrodesis was performed.
Treatment:
Amikacin 250 mg/ml
Daily dose administered: 6 ml
Days of treatment: 5 days
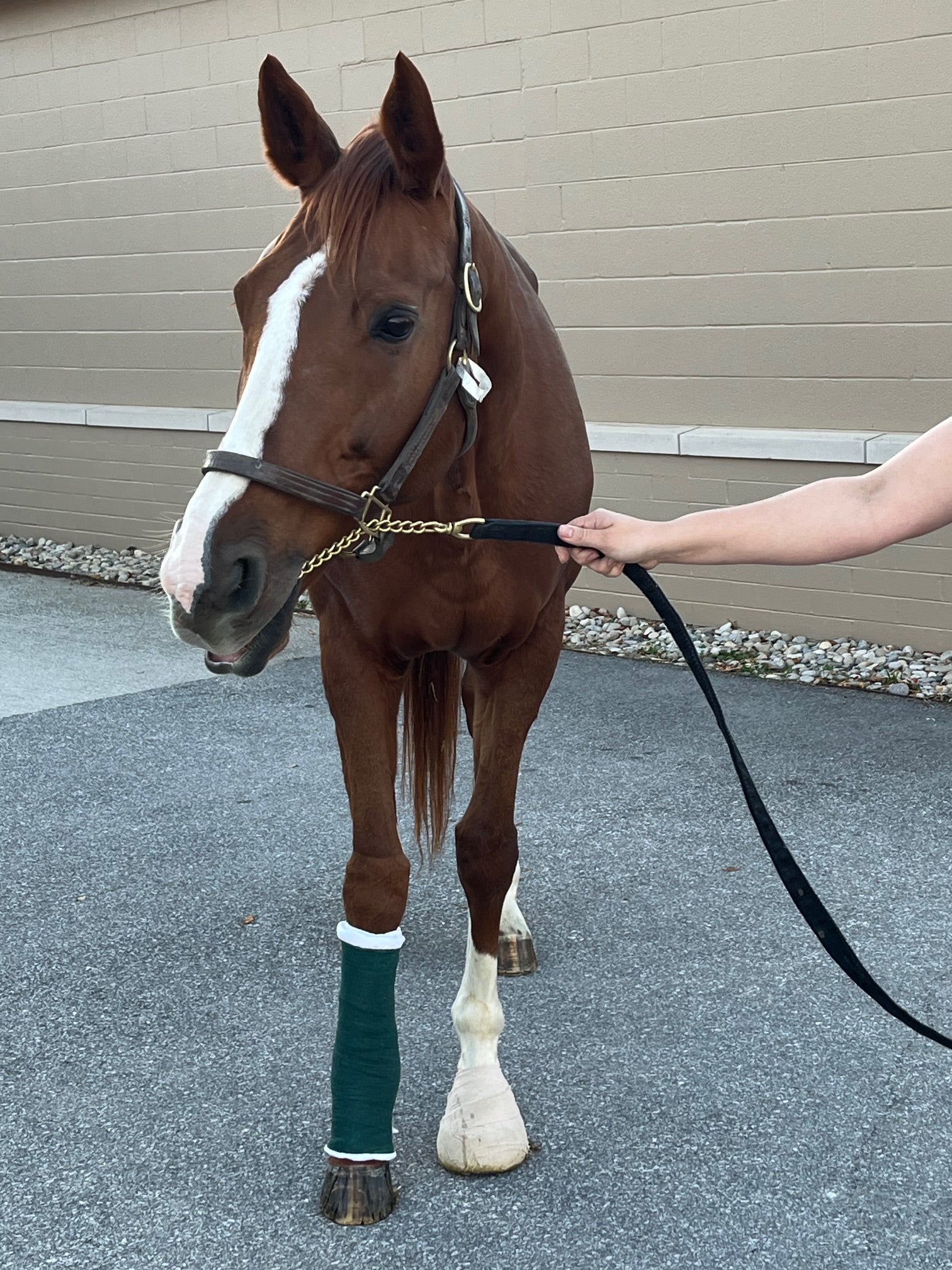
Conclusion: Vetlen Pouch worked well. The surgeon liked the ability to instill the antibiotics onto the plate for 5-days post-op. The mare has done well and is back home.
Images